中间件(通常)是一小段代码,它们接受一个请求,对其进行处理,每个中间件只处理一件事情,完成后将其传递给另一个中间件或最终处理程序,这样就做到了程序的解耦。
如果没有中间件那么我们必须在最终的处理程序中来完成这些处理操作,这无疑会造成处理程序的臃肿和代码复用率不高的问题。中间件的一些常见用例是请求日志记录,Header 操纵、HTTP 请求认证和 ResponseWriter 劫持等等。
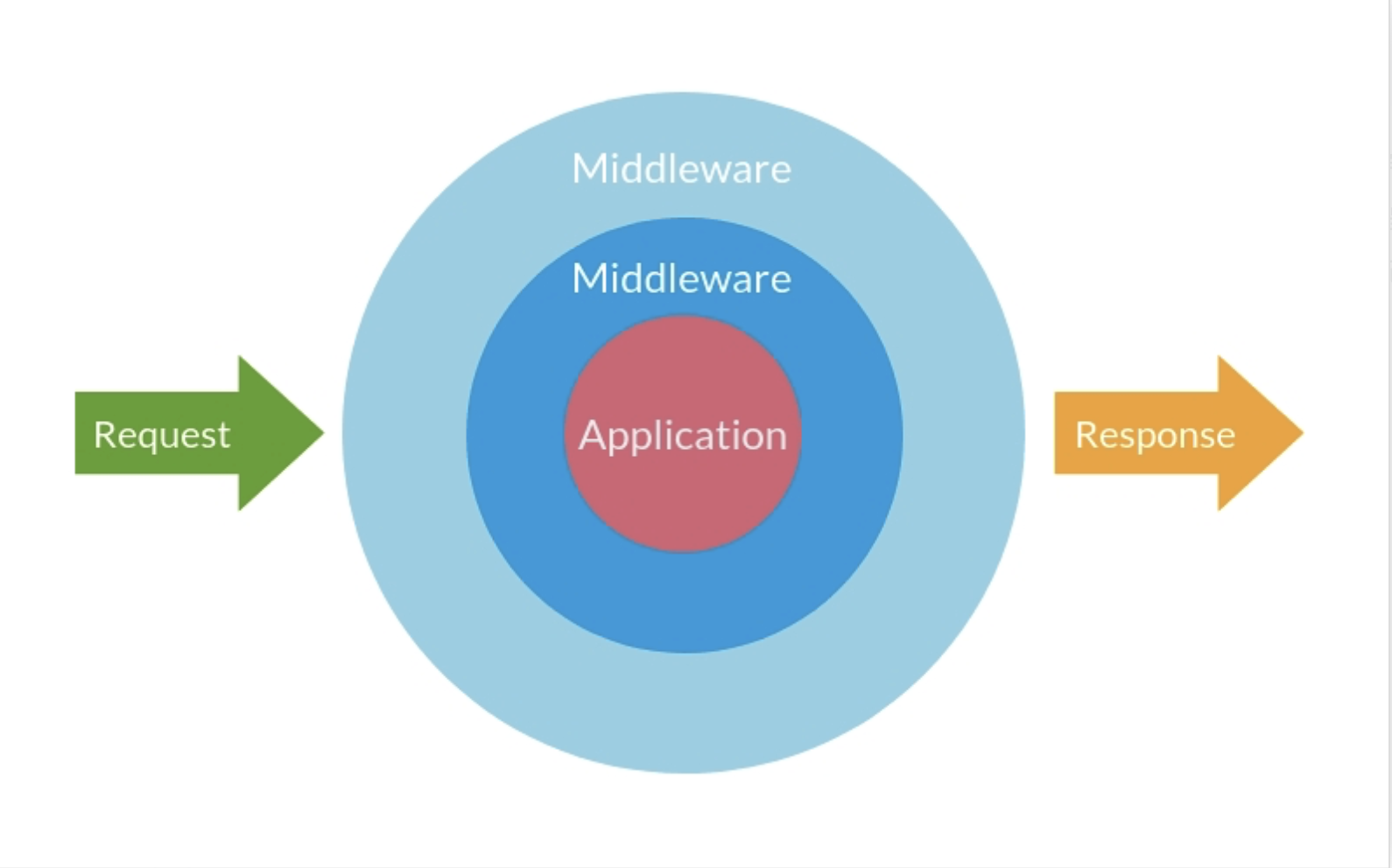
原理
在net/http包中可以看到定义了一个Handler接口
1
2
3
| type Handler interface {
ServeHTTP(ResponseWriter, *Request)
}
|
http.Handler 它 是 net/http 中定义的接口用来表示处理 HTTP 请求的对象,其对象必须实现 ServeHTTP 方法。
创建中间件
中间件只将 http.HandlerFunc 作为其参数,在中间件里将其包装并返回新的 http.HandlerFunc 供服务器服务复用器调用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| type Middleware func(http.HandlerFunc) http.HandlerFunc
func createNewMiddleware() Middleware {
// 创建一个新的中间件
middleware := func(next http.HandlerFunc) http.HandlerFunc {
// 创建一个新的handler包裹next
handler := func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 中间件的处理逻辑
......
// 调用下一个中间件或者最终的handler处理程序
next(w, r)
}
// 返回新建的包装handler
return handler
}
// 返回新建的中间件
return middleware
}
|
示例
使用beego调用中间件,记录日志示例
main.go
1
2
3
4
| //middle init
middles.Initialize(beego.AppConfig)
beego.RunWithMiddleWares("", middles.AccessMiddle)
|
Middles/middle.go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| package middles
import (
"bytes"
"github.com/sirupsen/logrus"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
"time"
)
//访问中间件,json格式记录接口请求及响应日志
func AccessMiddle(f http.Handler) http.Handler {
// 创建一个新的handler包装http.HandlerFunc
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
buf, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(r.Body)
rdr := ioutil.NopCloser(bytes.NewBuffer(buf))
//write
r.Body = rdr
logEntry := AccessLog.WithFields(logrus.Fields{
"access_time": time.Now(),
"ip": r.RemoteAddr,
"method": r.Method,
"path": r.RequestURI,
"query": r.URL.RawQuery,
"request_body": string(buf),
})
wc := &ResponseWithRecorder{
ResponseWriter: w,
statusCode: http.StatusOK,
body: bytes.Buffer{},
}
// 调用下一个中间件或者最终的handler处理程序
f.ServeHTTP(w, r)
//response_body 内容 需要在 ServeHTTP 后调用才会有值
defer logEntry.WithFields(logrus.Fields{
"status": wc.statusCode,
"response_body": wc.body.String(),
}).Info()
})
}
|
注意其request.body读取可能导致修改request.body
参考文章:Reading body of http.Request without modifying request state?
midddles/log.go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
| package middles
import (
"bytes"
"github.com/astaxie/beego/config"
"github.com/sirupsen/logrus"
"net/http"
"os"
)
var (
AccessLog *logrus.Logger
ErrorLog *logrus.Logger
accessLogFile = "./access.log"
errorLogFile = "./error.log"
)
func Initialize(cfg config.Configer) {
accessLogFile = cfg.String("log::access")
initAccessLog()
}
func initErrorLog() {
ErrorLog = logrus.New()
ErrorLog.SetFormatter(&logrus.JSONFormatter{})
file, err := os.OpenFile(errorLogFile, os.O_RDWR|os.O_CREATE|os.O_APPEND, 0755)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
ErrorLog.SetOutput(file)
}
func initAccessLog() {
AccessLog = logrus.New()
AccessLog.SetFormatter(&logrus.JSONFormatter{})
file, err := os.OpenFile(accessLogFile, os.O_RDWR|os.O_CREATE|os.O_APPEND, 0755)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
AccessLog.SetOutput(file)
}
type ResponseWithRecorder struct {
http.ResponseWriter
statusCode int
body bytes.Buffer
}
func (rec *ResponseWithRecorder) WriteHeader(statusCode int) {
rec.ResponseWriter.WriteHeader(statusCode)
rec.statusCode = statusCode
}
func (rec *ResponseWithRecorder) Write(d []byte) (n int, err error) {
n, err = rec.ResponseWriter.Write(d)
if err != nil {
return
}
rec.body.Write(d)
return
}
|
原文
Go Web 编程入门–编写 Web 中间件

